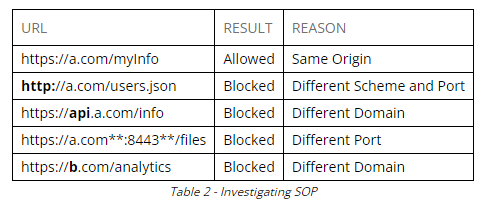
Browsers enforce a same-origin policy to prevent one origin from accessing resources on a different origin. An origin is defined as a protocol, hostname, and port number. A resource can be an image, html, data, json, etc.
This might seem confusing since plenty of websites have images, scripts, and other resources loaded from third-party origins. However, the purpose of SOP is not to prevent the request for a resource from being sent, but to prevent JavaScript from reading the response.
Images, iFrames, and other resources are allowed because while SOP doesn’t allow the JavaScript engine to access the contents of a response it does allow the resource to be loaded onto the page.
Try this code in the console as demonstration:
fetch("http://concord:8001/cfg.js")
.then(function (response) {
return response.text();
})
.then(function (text) {
console.log(text);
})
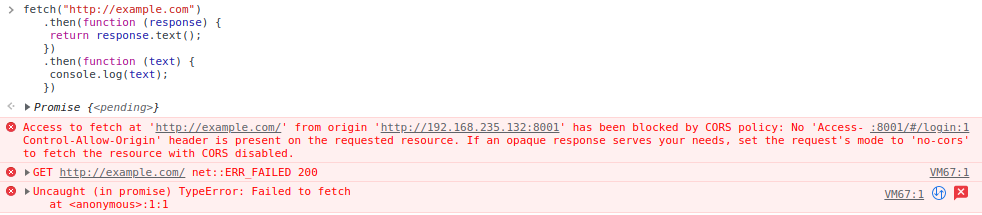
This would work however the following request will not work:
fetch("http://example.com")
.then(function (response) {
return response.text();
})
.then(function (text) {
console.log(text);
})