OSI Model
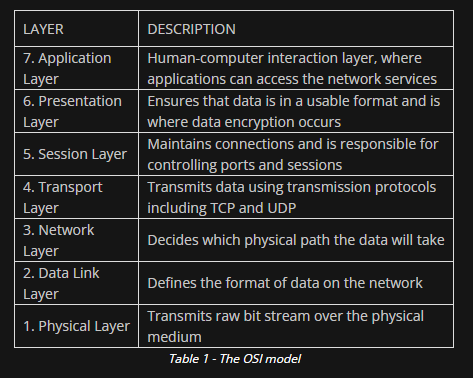
- Capturing wireless frames operate at layer 2.
MAC Frames
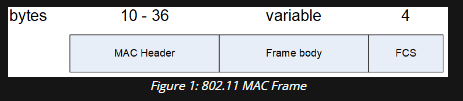
- Radiotap headers: Placed by the driver of the receiver and contains metadata for the specific frame
- MAC Header: Common fields for most frames
- Frame body: Carries data or contains additional information
- FCS (Frame Check Sequence): CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check, error detecting code) of the current wireless frame
MAC Header
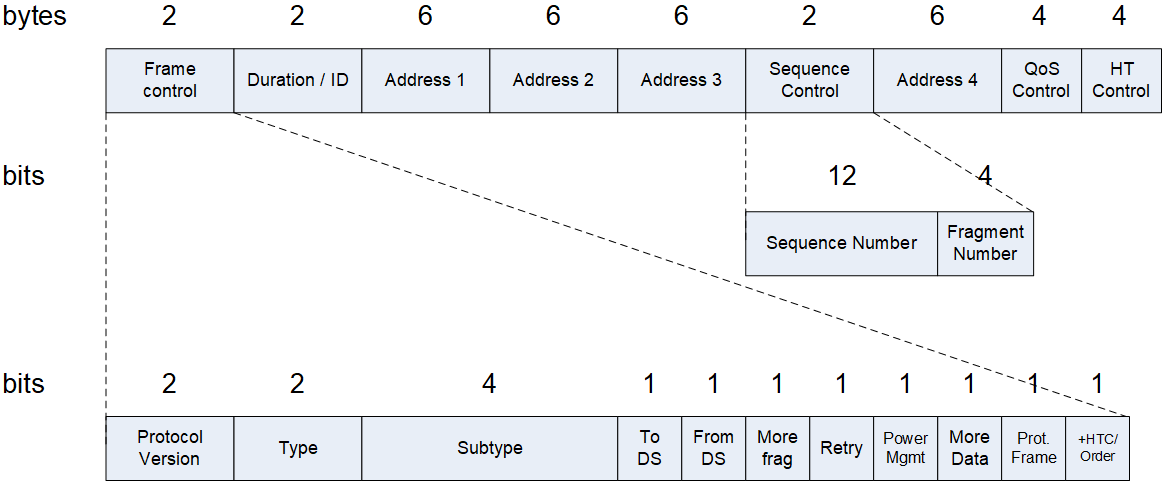
- Protocol Version
- Type - Management, Control, Data and Extension
- Subtype
- To DS and From DS (distribution system)
- More frag (more fragments after this)
- Retry
- Power Mgmt
- More data
- Protected Frame
- +HTC/Order (HT Control Field)
- Duration/ID: duration of the frame in microseconds
- Addresses: ToDS (client to AP), fromDS (AP to client)
- Sequence Control
- QoS Control and HT Control Fields
Frame Types
https://howiwifi.com/2020/07/13/802-11-frame-types-and-formats/
Management Frames
- Used to negotiate and control the relationship between APs and clients.
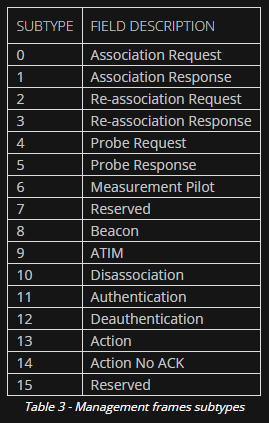
Beacon
- Common frames sent 10 times per second
- Broadcast by AP to ensure network sync
- Information: network name (unless SSID is hidden), the channel, the data rates available, type of encryption, and regulatory domain
Probe
- Used to scan for existing APs
- Sent by clients on multiple channels, which an AP will answer with a probe response about itself
Authentication
- Authentication frames used for connecting to the AP. Both client and AP use the authentication frame.
- Open Authentication is most common, otherwise there is Simultaneous Authentication of Equals (WPA3), and rarely shared authentication.
Association
- Association occurs after authentication frames.
Deauthentication
- Invalidates an authentication between client and AP.
Control Frames
- Help deliver data frames as well as other unicast frames
RTS/CTS
- https://dot11ap.wordpress.com/rtscts-and-cts-to-self-protocols/
- Supplement to the CSMA/CA mechanism that helps to reduce collisions.
ACK
- ACK frame tells client that the frame was received correctly.
Data Frames
Data
- Data frame such as DHCP request via UDP on an open network.
Null Data
- Consists only of MAC headers and a FCS.
Interacting with Networks
- Open network
- WEP
- WEP can be either open authentication or shared authentication. With open authentication, the process is identical to an open network.
- The main difference that we will note in the frames, is that the Privacy bit is set in the beacons, probe response, and association frames. The Privacy bit indicates encryption. Because of a lack of WPA or WPA2 tags in these frames, we also know that the security algorithm is WEP.
- EAPoL
- Extensible Authentication Protocol over LAN (EAPoL) frames
- Commonly used during the handshake when connecting to an AP with WPA, WPA2, WPA3, or OWE.
- Opportunistic Wireless Encryption (OWE) is a Wi-Fi standard which ensures that the communication between each pair of endpoints is protected from other endpoints.
